Ultium Battery Vs Lithium: Which Powers the Future Better?
Are you curious about the difference between Ultium batteries and traditional lithium batteries? Choosing the right battery can change how your devices or vehicles perform, how long they last, and even how much you spend.
You’ll discover what sets Ultium batteries apart from lithium ones, and why that matters for your next purchase. By the end, you’ll feel confident about which technology fits your needs best. Keep reading to unlock the secrets behind these powerful energy sources.

Credit: www.cnet.com
Ultium Battery Technology
The Ultium Battery Technology is a new step in electric vehicle power. It offers a fresh design to improve energy use and performance. This technology aims to provide longer drives and faster charging. It also focuses on safety and cost savings for users.
Composition And Design
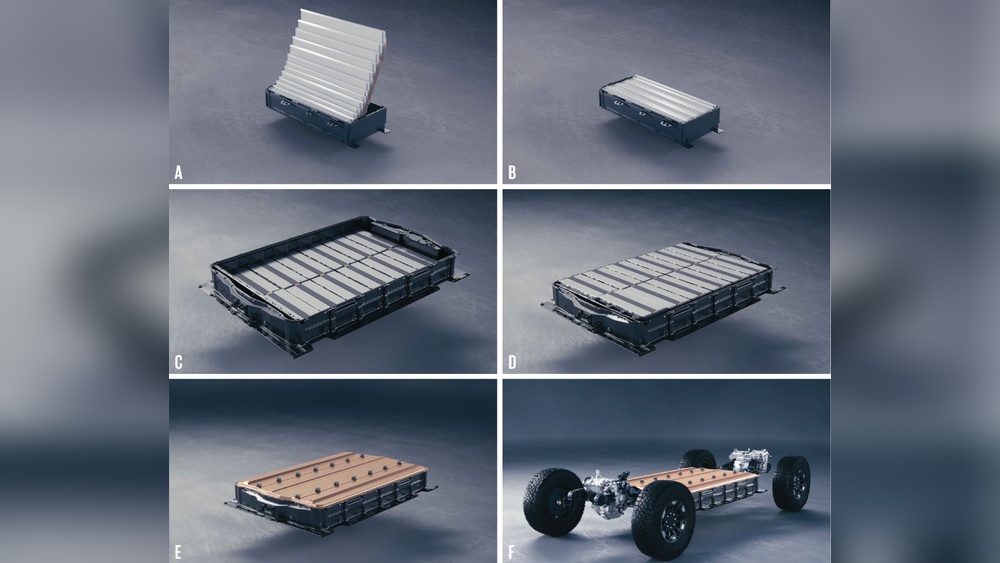
Ultium batteries use a mix of nickel, manganese, and cobalt. This mix helps balance cost and energy output. The design is modular, allowing different sizes for various vehicles. Stacking flat cells together reduces weight and space. This approach helps car makers create flexible battery packs.
Energy Density And Performance
Ultium batteries deliver high energy density, storing more power in less space. This means cars can drive farther on a single charge. The battery performs well in cold and hot weather. It also maintains energy over many charging cycles. This reliability supports daily use without quick wear.
Charging Speed And Efficiency
Ultium technology supports fast charging, cutting wait times. It can charge up to 80% in about 30 minutes. The battery manages heat well during charging, improving safety. Efficient energy use helps extend battery life. Drivers spend less time charging and more time on the road.
Lithium Battery Basics
Lithium batteries power many devices we use daily. They store energy in a small, light package. These batteries last longer than many other types. They charge quickly and provide stable power. Understanding lithium battery basics helps compare them with Ultium batteries.
Types And Variants
Lithium batteries come in several types. Lithium-ion is the most common for electronics. Lithium-polymer uses a gel-like electrolyte for flexible shapes. Lithium iron phosphate offers better safety and longer life. Each type suits different needs and devices.
Energy Storage Capabilities
Lithium batteries store energy efficiently. They have a high energy density. This means they hold more power in less space. They maintain voltage well during use. Their recharge cycles vary by type, but many last hundreds of charges.
Common Applications
Lithium batteries power smartphones, laptops, and tablets. They are in electric vehicles and power tools. Some use them in medical devices and cameras. Their light weight and strong power make them popular in many fields.
Comparing Lifespan And Durability
Understanding the lifespan and durability of Ultium and lithium batteries helps in choosing the right option. Both batteries power electric vehicles but differ in how long they last and how strong they stay over time.
These factors affect battery performance and overall vehicle reliability. Knowing the differences can save money and improve satisfaction.
Cycle Life
Cycle life means how many times a battery can fully charge and discharge. Ultium batteries often have a longer cycle life than standard lithium batteries. This means Ultium batteries last through more charge cycles without losing much capacity. A higher cycle life means the battery stays useful longer, reducing the need for early replacement.
Thermal Stability
Thermal stability shows how well a battery handles heat during use. Ultium batteries typically manage heat better than many lithium batteries. Good thermal stability reduces the risk of overheating and damage. It helps keep the battery safe and working well in hot or cold conditions.
Degradation Factors
Batteries lose capacity over time due to chemical changes. Ultium batteries degrade slower because of improved materials and design. Lithium batteries can degrade faster if exposed to high temperatures or frequent fast charging. Avoiding extreme conditions helps both batteries last longer. Understanding these factors helps users care for their batteries correctly.
Safety Considerations
Safety is a top concern for any battery technology. It affects users, manufacturers, and the environment. Understanding how Ultium batteries compare to traditional lithium batteries helps make safer choices. This section explains key safety considerations for both types.
Risk Of Overheating
Overheating can cause battery damage or failure. Lithium batteries sometimes get hot due to internal short circuits or high charging rates. Ultium batteries use a different design that helps control temperature better. Their modular structure spreads heat evenly. This lowers the chance of overheating.
Fire Hazards
Lithium batteries have a risk of catching fire if damaged or misused. The chemicals inside can ignite under certain conditions. Ultium batteries are made with safer materials that reduce fire risk. They also include layers that slow down or stop fires from spreading. This adds an extra layer of protection.
Safety Features
Both battery types include safety systems. Lithium batteries use sensors and circuits to prevent overcharging and short circuits. Ultium batteries add advanced cooling systems and robust casings. These features keep the battery stable and protect users. The design of Ultium batteries focuses on long-term safety and reliability.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of batteries is a key concern for many people. Batteries power electric cars and devices, but their production and disposal affect the planet. Comparing Ultium and lithium batteries helps us understand which is greener. This section looks at resource extraction, recycling, and carbon footprint.
Resource Extraction
Both Ultium and lithium batteries need metals like lithium, nickel, and cobalt. Mining these metals can harm land and water. Ultium batteries use less cobalt, which reduces some damage. Mining for lithium still raises concerns about water use and pollution. Efforts to find cleaner sources and reduce mining impacts are ongoing.
Recycling Processes
Recycling batteries lowers waste and saves raw materials. Lithium batteries have established recycling methods but can be complex. Ultium batteries are designed for easier recycling, with fewer toxic materials. Recycling helps recover metals and reduces the need for new mining. Improving recycling technology is crucial for both battery types.
Carbon Footprint
Carbon footprint measures greenhouse gas emissions from battery production and use. Ultium batteries often show a smaller carbon footprint due to efficient design. Manufacturing lithium batteries requires high energy, increasing emissions. Using clean energy in factories can cut these emissions. Both batteries help reduce emissions when used in electric vehicles.
Cost And Market Availability
Cost and market availability are key factors when comparing Ultium batteries and traditional lithium batteries. Both impact how widely these batteries are used and how affordable they are for consumers. Understanding these aspects helps to see which battery technology fits best for different needs.
Production Costs
Ultium batteries use a mix of materials that can lower production costs. They need less cobalt, a costly metal often used in lithium batteries. This reduction helps keep prices down. Traditional lithium batteries have higher costs due to expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing steps. Ultium’s design aims to simplify production and reduce waste, making it cheaper to produce in large amounts.
Market Adoption
Ultium batteries are gaining attention from car makers and manufacturers. Their flexible design fits many vehicle types, helping them enter the market faster. Lithium batteries have been popular for years and have a strong presence in many industries. Ultium still needs time to reach the same scale and availability as lithium batteries. Market trust and proven performance play big roles in adoption rates.
Future Pricing Trends
Prices for Ultium batteries are expected to drop as production grows. Mass production reduces costs and improves efficiency. Lithium battery prices may also fall but could face limits due to scarce materials. New technologies and recycling can affect prices for both types. The future may bring cheaper, more accessible battery options for consumers and businesses alike.
Applications And Future Potential
The applications of Ultium batteries and lithium batteries vary widely. Both types serve important roles today. Their future potential also shapes many industries. These batteries power devices, vehicles, and grids. Understanding their uses helps us see what lies ahead.
Electric Vehicles
Ultium batteries are designed for electric vehicles. They offer flexibility in size and shape. This helps car makers build different models. Lithium batteries also power many electric cars now. Ultium packs promise longer driving ranges. They can charge faster and last longer. This makes them attractive for future electric cars.
Grid Storage
Ultium and lithium batteries store energy for the grid. They help balance supply and demand. When renewable energy is high, batteries save power. When demand rises, batteries release power. Ultium batteries can scale well for large storage. Lithium batteries are common in smaller setups. Both types improve grid reliability and efficiency.
Consumer Electronics
Lithium batteries dominate in consumer electronics today. Phones, laptops, and tablets rely on them. Ultium batteries are bigger and less common here. They have potential for larger devices or new gadgets. Advances in battery tech could bring Ultium to electronics. This could offer longer use and faster charging.

Credit: www.youtube.com

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between Ultium And Lithium Batteries?
Ultium batteries use a modular design and nickel-cobalt-manganese chemistry. Lithium batteries typically rely on lithium-ion technology with various chemistries. Ultium offers better scalability and energy density, making it ideal for electric vehicles compared to traditional lithium batteries.
Are Ultium Batteries More Efficient Than Lithium Batteries?
Yes, Ultium batteries provide higher energy density and faster charging. They also offer improved thermal management and longer lifespan. This efficiency makes Ultium batteries more suitable for modern electric vehicles than standard lithium batteries.
Which Battery Is Safer: Ultium Or Lithium?
Ultium batteries have enhanced safety features, including advanced cooling systems. They reduce risks of overheating and thermal runaway compared to conventional lithium batteries. Thus, Ultium batteries are generally considered safer for electric vehicle applications.
Can Ultium Batteries Replace Lithium Batteries In Electric Cars?
Ultium batteries are designed to replace or improve upon lithium-ion batteries in EVs. They deliver better performance, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Many automakers are adopting Ultium technology to enhance electric car capabilities over traditional lithium batteries.
Conclusion
Ultium and lithium batteries both power many electric vehicles today. Ultium batteries offer flexible design and faster charging. Lithium batteries have proven technology and wide availability. Choosing the right battery depends on your needs and budget. Both types help reduce pollution and save energy.
Battery technology will keep improving in the future. Staying informed helps you make smart choices. Which battery fits you best? It’s up to your priorities and plans.