Dry Battery Vs Liquid Battery: Ultimate Comparison for Best Choice
When it comes to powering your devices, choosing the right battery can make all the difference. You might have heard about dry batteries and liquid batteries, but do you really know how they differ?
Understanding these differences can save you money, improve your device’s performance, and even protect your safety. You’ll discover what sets dry batteries apart from liquid batteries, how each works, and which one is best suited for your needs. Keep reading—you’ll be surprised by what you learn and how it can impact your everyday life.
Credit: wuling.id
Dry Battery Basics
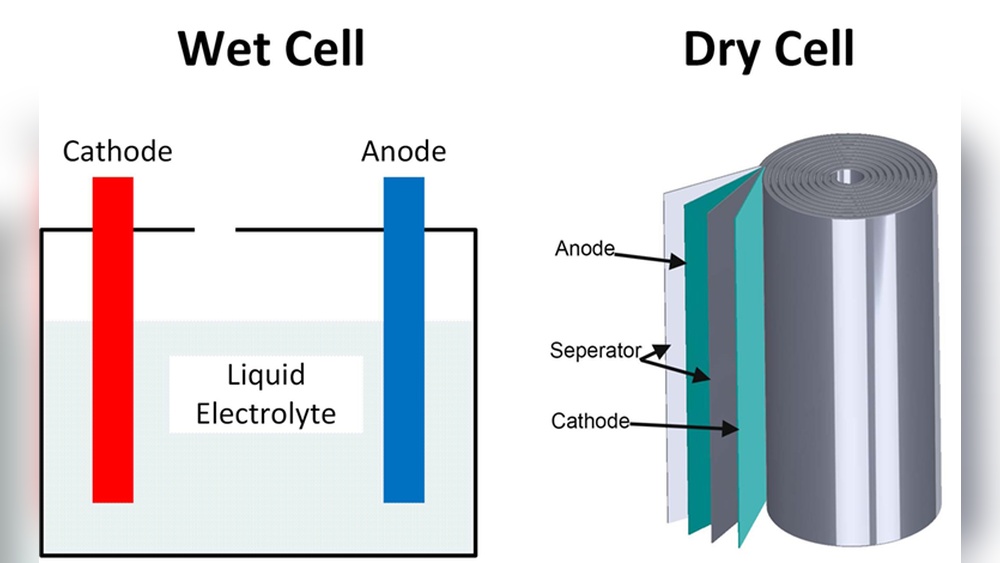
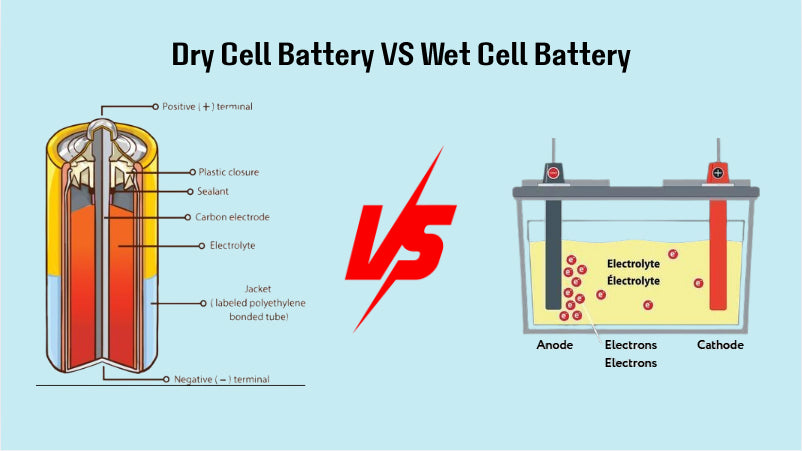
Dry batteries are common power sources in many devices. They differ from liquid batteries by using a paste or solid electrolyte instead of liquid. This design makes them safer and easier to handle. Understanding dry batteries helps in choosing the right power for everyday use.
Composition And Structure
Dry batteries contain a zinc anode and a carbon cathode. Between them lies a moist paste electrolyte. This paste carries ions to create an electric current. The solid or paste form stops leaks and spills. The battery casing is usually metal or plastic.
Common Types
Several dry battery types exist. The most popular is the alkaline battery, known for long life. Zinc-carbon batteries are cheaper but have less power. Lithium dry batteries offer high energy for small devices. Each type suits different needs and devices.
Advantages
Dry batteries are easy to use and transport. They do not spill, reducing mess and damage. These batteries work well in many temperatures. They have a long shelf life and low maintenance. Safe disposal is simpler than liquid batteries.
Credit: www.renogy.com
Liquid Battery Essentials
Liquid batteries use a fluid electrolyte to produce electrical energy. This liquid allows ions to move freely inside the battery. It helps create a flow of electricity. These batteries have unique features compared to dry batteries.
Understanding liquid batteries is important for choosing the right type. They are common in many applications, from cars to backup power. Knowing their basics helps you see how they work and why they last longer.
Electrolyte Characteristics
The electrolyte in liquid batteries is usually acidic or alkaline. It acts as a bridge for ions between electrodes. The liquid form allows easy ion flow, which boosts battery performance. The electrolyte’s strength affects battery life and power output.
Some electrolytes can be corrosive, needing careful handling. The liquid can also evaporate or spill if not sealed well. Proper maintenance keeps the battery working well over time.
Popular Varieties
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type of liquid battery. They use sulfuric acid as the electrolyte. These batteries power vehicles and store energy for solar systems.
Nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries also use liquid electrolytes. They offer good performance for portable devices and tools. Each type has specific uses based on its design and cost.
Benefits
Liquid batteries can deliver high power for short periods. They are usually cheaper to produce than dry batteries. Their design allows easy recharging and long cycle life.
These batteries handle large currents well, making them ideal for cars. They can also be recycled, reducing environmental impact. Proper care extends their usability and safety.
Performance Comparison
Comparing dry batteries and liquid batteries reveals important differences in their performance. Each type has unique strengths and weaknesses. These factors affect their use in various devices and systems. Understanding performance helps choose the right battery for specific needs.
Energy Density
Energy density measures how much energy a battery holds in a small space. Dry batteries usually have lower energy density. Liquid batteries can store more energy in the same size. This makes liquid batteries better for high-capacity uses. Dry batteries suit smaller gadgets with less energy demand.
Charge And Discharge Rates
Charge and discharge rates show how fast a battery fills or releases energy. Dry batteries can charge and discharge quickly. This works well for devices needing bursts of power. Liquid batteries often charge slower but can deliver steady power longer. They perform well in applications needing constant energy.
Lifespan And Durability
Battery lifespan means how long it lasts before failing. Dry batteries tend to have shorter lifespans. They wear out faster with repeated use. Liquid batteries last longer and handle more charge cycles. Dry batteries are less durable under tough conditions. Liquid batteries resist damage better and keep working over time.

Credit: www.motorcyclevalley.com
Safety And Environmental Impact
Safety and environmental impact are key factors in choosing between dry and liquid batteries. Both types store energy but behave differently in use and disposal. Understanding these differences helps protect people and nature.
Hazards And Risks
Dry batteries are sealed and less likely to leak harmful substances. They pose low risk of acid burns. Liquid batteries contain corrosive fluids that can spill if damaged. These fluids can cause skin burns and damage surfaces. Both batteries can catch fire if short-circuited or overheated. Handling batteries with care reduces these dangers.
Disposal And Recycling
Improper disposal of batteries harms the environment. Dry batteries often contain heavy metals like mercury or cadmium. These metals can pollute soil and water if thrown away carelessly. Liquid batteries require special recycling due to their acid content. Many places offer battery recycling programs. Recycling recovers valuable materials and prevents pollution.
Eco-friendliness
Dry batteries generally have a smaller environmental footprint during use. They last longer and leak less. Liquid batteries need more maintenance and have higher spill risks. Both types use toxic materials that impact the planet if not managed well. Choosing rechargeable options reduces waste. Proper disposal and recycling support a healthier environment.
Cost And Availability
Cost and availability play key roles in choosing between dry batteries and liquid batteries. These factors affect both buyers and manufacturers. Understanding these differences helps make smarter decisions for various uses.
Manufacturing Costs
Dry batteries usually cost less to produce. They use solid materials and simpler processes. Liquid batteries need special chemicals and careful handling. This raises their production price. Factories require more safety measures for liquid batteries.
Market Presence
Dry batteries are widely available worldwide. Most stores stock them for everyday devices. Liquid batteries are less common and often found in specific industries. Their availability depends on demand and location. Dry batteries remain easier to find for regular users.
Maintenance Expenses
Dry batteries need little to no maintenance. Once sealed, they work until drained. Liquid batteries require regular checks to avoid leaks or damage. Repairs and fluid replacements add to long-term costs. These upkeep needs can increase overall expenses.
Best Use Cases
Batteries power many devices and systems around us. Choosing the right type depends on the use case. Dry batteries and liquid batteries serve different needs. Understanding their best use cases helps in making smart choices.
Portable Electronics
Dry batteries fit well in small gadgets. Toys, remote controls, and flashlights often use dry cells. They are light and easy to carry. Dry batteries do not leak easily, making them safe for handheld devices. Their compact size suits portable electronics perfectly.
Automotive Applications
Liquid batteries, like lead-acid types, power most cars. They provide high current needed to start engines. These batteries handle temperature changes well. Liquid batteries are easy to recharge and maintain. Their design supports heavy use and long life in vehicles.
Grid Storage Solutions
Liquid batteries excel in storing large amounts of energy. They are common in solar and wind power systems. These batteries store energy for use during peak demand. Liquid types allow easier scaling for big storage needs. Their efficiency keeps the power grid stable and reliable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between Dry And Liquid Batteries?
Dry batteries use a solid or paste electrolyte, while liquid batteries contain a liquid electrolyte. This affects their design, maintenance, and application.
Which Battery Type Is More Environmentally Friendly?
Dry batteries are generally more eco-friendly. They have less risk of leakage and are easier to recycle compared to liquid batteries.
Are Dry Batteries Safer Than Liquid Batteries?
Yes, dry batteries are safer as they pose less risk of acid spills or leaks, reducing hazards during handling and use.
Which Battery Lasts Longer, Dry Or Liquid?
Liquid batteries usually have a longer lifespan due to better electrolyte flow, but dry batteries offer convenience and lower maintenance.
Conclusion
Dry batteries and liquid batteries each have clear uses and limits. Dry batteries are easy to carry and safe for small devices. Liquid batteries offer longer life and better power for big machines. Choosing the right battery depends on your needs and conditions.
Think about size, cost, and how long you need power. Both types play important roles in everyday life. Knowing their differences helps you pick wisely. Simple and smart choices save time and money.