3 Phase Vs Single Phase Generator: Which is Right for You?
Choosing the right generator is crucial for your power needs. There are two main types: 3-phase and single-phase generators.
Understanding the differences can help you make an informed decision. Generators play a vital role in providing backup power during outages. They also supply energy in remote areas without access to the grid. Deciding between a 3-phase and a single-phase generator depends on various factors.
These include your power requirements, budget, and specific applications. This comparison will help you understand the key features of each type. It will also highlight their advantages and limitations. Whether you need a generator for home, business, or industrial use, knowing the difference is essential. Let’s dive into the details to find the best option for your needs.
Introduction To Generators
Generators come in two types: single phase and three phase. Three phase generators are more efficient for industrial use. Single phase generators are simpler and often used for homes and small businesses.
Generators are vital in many applications. They provide power during outages and in remote areas. Understanding the basics helps in choosing the right one.Purpose And Function
Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process is essential during power failures. They ensure continuous operation of devices and systems. Different generators serve various needs. Portable generators are common for homes. Industrial generators support factories and large buildings.Types Of Generators
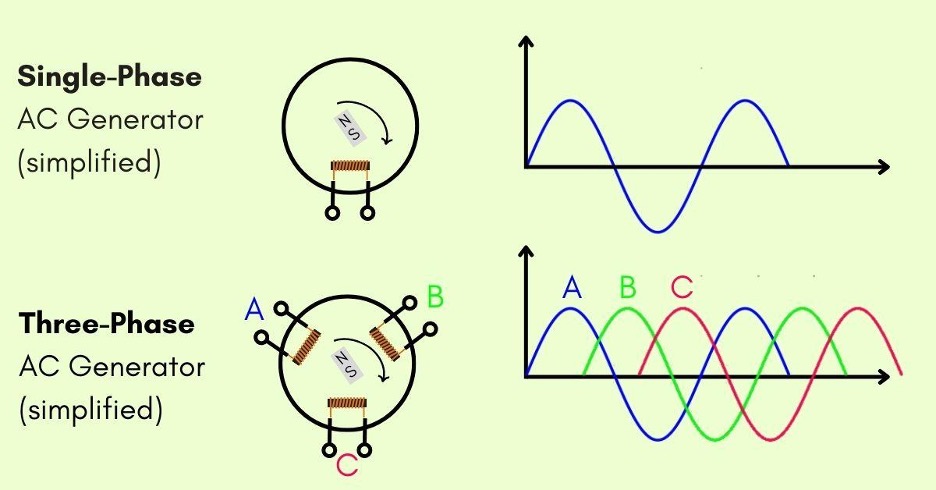
There are two main types: single phase and three phase generators. Single phase generators are simple and suitable for small loads. They are often used in homes and small businesses. Three phase generators are more complex. They are ideal for industrial and large-scale operations. Each type has its own advantages and applications. Understanding these helps in making an informed choice. “`
Credit: woodstockpower.com
Basics Of Single Phase Generators
Single-phase generators are widely used for small to medium power needs. They are simple to operate and maintain. These generators are perfect for homes, small offices, and light industrial applications. Understanding their basics helps in choosing the right generator for your needs.
How They Work
Single-phase generators produce electricity using a single alternating current (AC) waveform. They have two main components: the stator and the rotor. The stator is stationary and contains coils of wire. The rotor rotates inside the stator and creates a magnetic field.
As the rotor spins, it induces an AC voltage in the stator coils. This voltage is then used to power electrical devices. Single-phase generators typically produce power at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz, depending on the region.
Common Applications
Single-phase generators are ideal for a variety of applications. Here are some common uses:
- Residential Use: Power backup for homes during outages.
- Small Offices: Ensures continuous operation of essential equipment.
- Light Industrial: Suitable for small workshops and tools.
- Recreational: Power for camping, RVs, and outdoor events.
In residential settings, they can run essential appliances like refrigerators, lights, and fans. For small offices, they ensure computers and communication devices stay operational. Light industrial applications might include running small machinery and power tools.
In recreational use, they provide power for camping trips and outdoor events. Single-phase generators are versatile and reliable for these applications.
Basics Of Three Phase Generators
Three phase generators are vital in many industries. They provide efficient and reliable power. Understanding their basics helps to see why they are preferred over single phase generators.
How They Work
Three phase generators produce power using three alternating currents. These currents are evenly spaced in their cycle. This creates a constant and reliable power flow. The power is smoother and more efficient. It reduces the risk of power dips.
These generators use three coils. Each coil generates a separate current. The currents are combined to create a stable output. This output is perfect for heavy-duty applications. It also ensures that power delivery remains consistent.
Common Applications
Three phase generators are common in industrial settings. Factories and large buildings use them. They power heavy machinery and equipment. These generators also supply power to data centers.
They are also used in hospitals. Reliable power is critical in healthcare. Three phase generators ensure that life-saving equipment runs without interruption.
Commercial buildings use them too. They power elevators, HVAC systems, and large electrical appliances. This makes them essential in many sectors.

Credit: www.auroragenerators.com
Comparing Power Output
Comparing the power output of single-phase and three-phase generators helps understand their usage. Both generator types have their unique advantages and applications. This section will explore the power output differences of single-phase and three-phase generators in detail.
Single Phase Output
A single-phase generator produces power using one alternating current (AC) waveform. It is simple and reliable. Single-phase generators are common in residential settings. They are suitable for small appliances and light electrical loads. They provide a consistent and stable power supply for most household needs. Single-phase generators are typically used for lower power requirements.
Three Phase Output
A three-phase generator generates power through three alternating currents (AC) waveforms. It offers a higher and more efficient power output. Three-phase generators are often used in industrial and commercial settings. They can handle heavier loads and provide a balanced power supply. This makes them ideal for running large machines and equipment. The power output is more consistent and efficient compared to single-phase generators.
Efficiency And Performance
Choosing between a 3 phase and a single phase generator can impact efficiency and performance. This section delves into how each type fares in terms of energy efficiency and load handling. Understanding these aspects can help you make an informed decision for your power needs.
Energy Efficiency
3 phase generators are generally more energy-efficient. They produce more power using less fuel. This makes them ideal for industrial applications. With three alternating currents, the energy output is consistent and reliable.
Single phase generators, on the other hand, are often less efficient. They use more fuel to produce the same amount of power. This can lead to higher operational costs over time. They are better suited for smaller, less demanding applications.
Load Handling
3 phase generators excel at handling larger loads. They distribute the electrical load more evenly. This results in smoother and more stable power delivery. Industries that require heavy machinery benefit greatly from this.
Single phase generators struggle with larger loads. They are better for lighter loads. Residential use, small offices, and light commercial applications are their forte. Overloading a single phase generator can lead to performance issues and potential damage.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Aspect | 3 Phase Generator | Single Phase Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High | Low |
| Load Handling | Excellent | Good for light loads |

Credit: www.bisonindustry.com
Installation And Maintenance
Understanding the installation and maintenance of generators is crucial. It ensures optimal performance and longevity. Let’s delve into the specifics of setting up and maintaining 3 phase and single phase generators.
Setup Requirements
Setting up a 3 phase generator requires more expertise. It has complex wiring and connections. Professional installation is often needed. On the other hand, single phase generators are simpler to set up. They have straightforward wiring, making DIY installation possible.
Maintenance Needs
Maintenance for 3 phase generators involves checking each phase. Ensuring balance is critical to avoid damage. Regular inspections by a technician are recommended. Single phase generators have simpler maintenance. Basic checks and occasional servicing keep them running smoothly.
Both types of generators need routine oil changes. Also, regular filter replacements are necessary. Keeping the generator clean prevents debris buildup. This ensures efficient operation.
Cost Considerations
Choosing between a 3 Phase and Single Phase Generator involves understanding the costs. These costs can be divided into the initial investment and long-term costs. Each type of generator has its own set of expenses. Let’s explore these in detail.
Initial Investment
The initial cost of a generator is a crucial factor. Single Phase Generators generally have a lower initial cost. They are simpler in design and easier to manufacture. This makes them more affordable for small businesses and homes.
In contrast, 3 Phase Generators have a higher initial cost. They are more complex and provide more power. This makes them suitable for industrial applications. If your business needs high power, a 3 Phase Generator is a better investment despite the higher initial cost.
Long-term Costs
When considering long-term costs, maintenance and operational efficiency are key. Single Phase Generators have lower maintenance costs. They are less complex and require fewer repairs. This makes them ideal for less frequent use.
3 Phase Generators might have higher maintenance costs. Yet, they are more efficient in the long run. They consume less fuel for the same output. This efficiency can offset the higher maintenance costs over time.
The longevity of a generator also affects long-term costs. 3 Phase Generators typically last longer. Their robust design can handle more wear and tear. This makes them a more cost-effective choice for continuous use.
To summarize the long-term costs, consider the table below:
| Generator Type | Maintenance Costs | Fuel Efficiency | Longevity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Phase | Lower | Less Efficient | Shorter Lifespan |
| 3 Phase | Higher | More Efficient | Longer Lifespan |
In conclusion, both 3 Phase and Single Phase Generators have their own cost benefits. It’s important to weigh the initial investment against the long-term costs. This will help you make the best choice for your needs.
Choosing The Right Generator
Choosing the right generator is crucial for ensuring a reliable power supply. Whether you need it for your home, business, or industrial use, understanding the differences between 3-phase and single-phase generators is important. This section will help you make an informed decision.
Assessing Your Needs
Start by assessing your power needs. Consider the following:
- Total power requirement: Calculate the total wattage of all devices.
- Type of devices: Identify if they are sensitive electronics or heavy machinery.
- Usage duration: Determine how long you need the generator to run.
For homes and small businesses, a single-phase generator is often sufficient. It provides stable power for lights, refrigerators, and small appliances.
Industrial applications usually require a 3-phase generator. These are better suited for heavy machinery and large-scale operations. They provide a higher and more stable power output.
Expert Recommendations
Experts recommend considering the following factors:
- Power Load: Match the generator to your total power load.
- Installation: Ensure you have the proper setup for either generator type.
- Maintenance: Check the maintenance requirements. 3-phase generators may need more upkeep.
Consulting with a professional can provide valuable insights. They can help you assess your power needs and recommend the best generator type.
Case Studies And Examples
When deciding between a single-phase and a three-phase generator, examining real-world applications can help. Both types serve different needs, providing unique benefits for various scenarios. Let’s explore some case studies and examples.
Residential Use
Single-phase generators are popular in homes. They provide adequate power for most household appliances. For example, a family living in a suburban area uses a single-phase generator during power outages. It runs their refrigerator, lights, and a few electronic devices. The generator is easy to start and maintain. It fits well with their daily needs.
Three-phase generators in homes are less common. They are usually found in large estates or homes with high power needs. For instance, a large mansion with a home theater, gym, and extensive outdoor lighting might use a three-phase generator. This setup ensures all systems run smoothly without overloading.
Industrial Use
Industries often require three-phase generators. These generators handle heavy loads and provide stable power. Take a manufacturing plant as an example. It uses a three-phase generator to power machines, conveyor belts, and other equipment. The generator’s efficiency ensures continuous operation without interruptions.
In contrast, small workshops might use single-phase generators. A local bakery with basic equipment could run on a single-phase generator. It powers ovens, mixers, and lights efficiently. This setup is cost-effective and meets their power needs.
Understanding these examples can guide the right choice for your specific needs. Whether for a home or industry, selecting the appropriate generator type ensures efficient power supply.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Single-phase Generator?
A single-phase generator produces AC power using a single alternating voltage. It’s ideal for small loads and residential use.
How Does A Three-phase Generator Work?
A three-phase generator produces power using three alternating currents, offset by 120 degrees. It is efficient for industrial applications.
Which Is More Efficient, Single-phase Or Three-phase?
Three-phase generators are more efficient. They provide smoother power delivery and are ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Can I Use A Three-phase Generator At Home?
Yes, but it’s usually unnecessary. Single-phase generators are sufficient for typical household appliances and needs.
Conclusion
Choosing between a 3 phase and single phase generator depends on your needs. Three-phase generators offer more power and efficiency. They are ideal for industrial use. Single-phase generators work well for homes and small businesses. They are easier to install and maintain.
Consider your power requirements before deciding. Assess your budget and application. Both types have their benefits. Make an informed choice for reliable power.