Diesel Generator Vs Gasoline Generator: Which is Better?
When considering power backup options, diesel and gasoline generators are popular choices. Each type has unique benefits and drawbacks.
Choosing between a diesel generator and a gasoline generator can be challenging. Both serve the same purpose, but their differences can impact performance, cost, and suitability. Diesel generators are known for durability and fuel efficiency, often used in industrial settings.
Gasoline generators, on the other hand, are typically more affordable and lighter, making them ideal for home use and smaller applications. Understanding the key differences can help you make an informed decision. This comparison aims to clarify the main aspects of each type, helping you choose the best generator for your needs.

Credit: www.bisonindustry.com
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a critical factor to consider when choosing a generator. It affects operational costs and environmental impact. Comparing diesel and gasoline generators helps determine which is more economical and eco-friendly. Let’s dive into the specifics of each fuel type.
Diesel Efficiency
Diesel generators are known for their superior fuel efficiency. They often consume less fuel than gasoline models. This makes them a preferred choice for long-term use.
A diesel engine operates at a higher compression ratio. This leads to better thermal efficiency. As a result, diesel generators convert more fuel into energy. This reduces fuel consumption and operational costs.
Here is a comparison table to illustrate fuel consumption:
| Generator Type | Fuel Consumption (Liters/Hour) |
|---|---|
| Diesel | 0.4 – 0.6 |
| Gasoline | 0.6 – 1.0 |
Gasoline Efficiency
Gasoline generators are less fuel-efficient than diesel counterparts. They burn more fuel for the same power output. This leads to higher operational costs.
Gasoline engines have a lower compression ratio. This results in less thermal efficiency. They convert less fuel into energy, increasing consumption.
Key points to consider:
- Gasoline is more volatile, leading to faster consumption.
- Higher fuel costs over long-term use.
Despite these drawbacks, gasoline generators have their advantages. They are lighter, quieter, and more portable. This makes them suitable for short-term or emergency use.
Cost Analysis
When selecting a generator, cost analysis is critical. Consider both the initial purchase cost and long-term operating costs. Understanding these factors helps you make an informed decision.
Initial Purchase Cost
The initial purchase cost of a generator varies significantly between diesel and gasoline types.
| Generator Type | Average Initial Cost |
|---|---|
| Diesel Generator | $3,000 – $15,000 |
| Gasoline Generator | $500 – $5,000 |
Diesel generators are typically more expensive upfront. They range from $3,000 to $15,000.
Gasoline generators are generally cheaper. They range from $500 to $5,000.
Long-term Operating Costs
Long-term operating costs include fuel, maintenance, and repairs. These costs can add up over time.
- Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines are more fuel-efficient. They consume less fuel per hour.
- Maintenance: Diesel generators require less frequent maintenance. They have fewer parts that wear out.
- Repairs: Gasoline engines may need more frequent repairs. Their parts wear out faster.
Diesel generators offer lower fuel costs and maintenance expenses in the long run. Gasoline generators may have higher costs in these areas.
Consider both the initial purchase cost and the long-term operating costs when choosing your generator. These factors significantly impact your total investment.
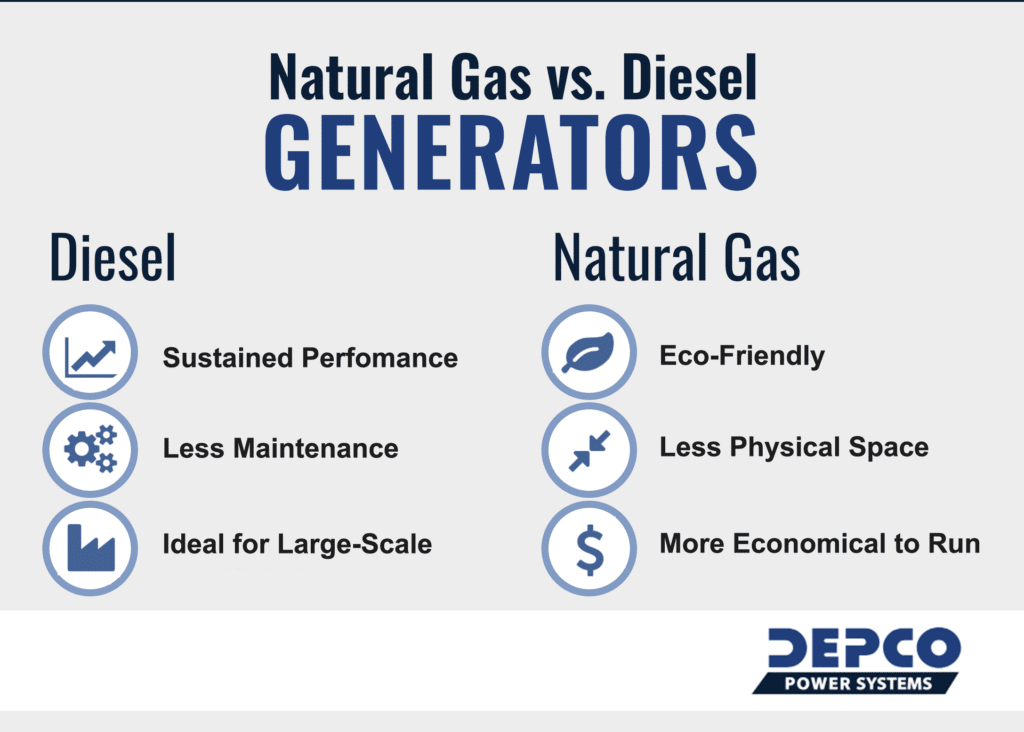
Performance
Performance is a crucial factor when choosing a generator. Diesel and gasoline generators differ significantly in their power output and reliability. Understanding these differences helps in making an informed decision.
Power Output
Diesel generators typically offer higher power output compared to gasoline generators. They are designed to handle heavy loads and are suitable for industrial and commercial use.
Gasoline generators are generally more suitable for lighter loads. They work well for small businesses and home use.
| Generator Type | Power Output | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Diesel | High | Industrial, Commercial |
| Gasoline | Medium to Low | Residential, Small Business |
Reliability
Diesel generators are known for their durability and long lifespan. They require less maintenance and are less likely to break down.
Gasoline generators tend to require more maintenance. They have a shorter lifespan and are more prone to wear and tear.
- Diesel generators: Long lifespan, less maintenance.
- Gasoline generators: Shorter lifespan, more maintenance.
Both types have their advantages. Diesel generators excel in providing robust and reliable power. Gasoline generators are often more convenient for smaller, short-term needs.
Credit: www.depco.com
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is vital for keeping generators in good working condition. Diesel and gasoline generators have distinct maintenance needs. Understanding these can help you choose the right one for your needs.
Diesel Maintenance Needs
Diesel generators are known for their durability. They need less frequent maintenance compared to gasoline generators. Diesel engines are built to last longer. They often run at lower RPMs, reducing wear and tear. Regular oil changes are crucial. Check and replace oil filters to ensure smooth operation. Inspect the air filters regularly. Clean or replace them as needed to keep the engine running efficiently. Monitor coolant levels to prevent overheating. Diesel engines also need periodic fuel system checks. Clean the fuel injectors to maintain performance. Always use high-quality diesel fuel to minimize deposits and contamination. Ensure the battery is in good condition. Check the connections and charge it regularly. Diesel generators may need professional servicing occasionally. This ensures all components are in top shape.
Gasoline Maintenance Needs
Gasoline generators require more frequent maintenance. They are often used for short-term power needs. Regular oil changes are essential. This keeps the engine running smoothly. Replace the oil filter often to prevent clogging. Check the air filter regularly. Clean or replace it to maintain efficiency. Gasoline engines can be prone to carbon buildup. Clean the spark plug regularly to prevent issues. Gasoline degrades faster than diesel. Use fresh fuel to avoid performance problems. Add a fuel stabilizer if storing the generator for long periods. Inspect the fuel lines for cracks or leaks. Replace them if damaged. Ensure the battery is charged and in good condition. Gasoline generators may need more frequent professional servicing. This helps in identifying and fixing potential problems early.
Environmental Impact
Choosing between a diesel and gasoline generator often involves considering their environmental impact. Understanding how each type affects the environment can help you make an informed decision.
Emissions
Diesel generators typically produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM). These emissions contribute to air pollution and can harm human health. On the other hand, gasoline generators emit more carbon monoxide (CO) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Here is a comparison of emissions from diesel and gasoline generators:
| Emission Type | Diesel Generators | Gasoline Generators |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) | High | Moderate |
| Particulate Matter (PM) | High | Low |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Low | High |
| Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) | Moderate | High |
Fuel Spills And Leaks
Fuel spills and leaks can happen with both diesel and gasoline generators. Diesel fuel is less flammable, making it somewhat safer. Gasoline, being more volatile, poses a higher risk of fire and explosion.
Consider these points regarding fuel spills and leaks:
- Diesel fuel is more biodegradable than gasoline.
- Gasoline spills can contaminate soil and water faster.
- Proper storage and handling reduce the risk of spills for both types.
Both types of generators require careful handling to minimize environmental damage.
Safety Considerations
When choosing between a diesel generator and a gasoline generator, safety is a critical factor. Each type has unique safety considerations that must be understood and managed. This section will explore the safety aspects of both generators under two main headings: Fire Hazards and Handling and Storage.
Fire Hazards
Both diesel and gasoline generators present fire risks. However, the nature of the risks differs.
- Diesel Generators: Diesel fuel is less flammable than gasoline. This reduces the risk of accidental fires. Diesel has a higher flash point, making it safer for storage and use.
- Gasoline Generators: Gasoline is highly flammable. This increases fire risks during storage and operation. Proper handling is crucial to prevent accidents.
It’s important to follow safety guidelines for both types. Keep generators away from flammable materials. Always have a fire extinguisher nearby.
Handling And Storage
Safe handling and storage are essential for both diesel and gasoline generators. Here’s a comparison:
| Generator Type | Handling | Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Diesel Generator | Heavier and more robust. Requires careful handling. | Store in cool, dry places. Less risk of evaporation. |
| Gasoline Generator | Lighter and easier to move. Handle with caution. | Store in well-ventilated areas. High risk of vapor build-up. |
Always use approved containers for fuel storage. Regularly inspect generators for leaks or damage. Proper handling and storage reduce risks and ensure safety.
Application Scenarios
Choosing between a diesel generator and a gasoline generator depends on the application. Both have unique advantages and drawbacks. Understanding where each type excels can help make an informed decision.
Residential Use
Diesel generators offer more durability for home use. They can run for longer periods. This makes them ideal for extended power outages. Diesel fuel is also safer and less flammable. But, they can be noisy and costly.
Gasoline generators are perfect for short-term use. They are quieter and cheaper. They are also easy to start and maintain. But, gasoline is highly flammable and has a shorter shelf life.
Commercial And Industrial Use
Diesel generators dominate in commercial and industrial settings. They are reliable and fuel-efficient. They handle heavy loads for long durations. This makes them perfect for construction sites and hospitals.
Gasoline generators are less common in these settings. They are best for smaller, less demanding tasks. They serve well as backup generators for small businesses. They are easy to transport and set up.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Differences Between Diesel And Gasoline Generators?
Diesel generators are more fuel-efficient and durable. Gasoline generators are quieter and easier to start. Diesel is better for long-term use, while gasoline is suited for short-term needs.
Which Generator Is More Fuel-efficient?
Diesel generators are more fuel-efficient. They consume less fuel and offer longer operational hours. This makes them cost-effective for continuous usage.
Are Diesel Generators More Durable Than Gasoline Generators?
Yes, diesel generators are generally more durable. They have a longer lifespan due to robust construction and better cooling systems. Ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Which Generator Is Easier To Maintain?
Gasoline generators are easier to maintain. They have fewer components and simpler mechanics. Diesel generators require more frequent servicing and specialized maintenance.
Conclusion
Both diesel and gasoline generators have their advantages. Diesel generators are more fuel-efficient. They last longer and require less maintenance. Gasoline generators are cheaper and easier to start. They are also more portable. Your choice depends on needs and budget.
Each type serves different purposes well. Consider your priorities carefully. Make an informed decision. You’ll get the best generator for your needs.







