Agm Battery Vs Lithium: Ultimate Comparison for Power and Performance
When it comes to choosing the right battery for your needs, you might find yourself stuck between AGM batteries and lithium batteries. Which one will give you better performance, last longer, and save you money?
Understanding the key differences can make a huge impact on your decision—and your experience. You’ll discover the pros and cons of each option, so you can confidently pick the battery that fits your lifestyle and power demands perfectly. Ready to find out which battery truly powers your future?
Keep reading.

Credit: www.victronenergy.com
Battery Basics
Batteries store energy to power many devices. Understanding their types helps choose the right one. AGM and lithium batteries are common choices. Each has a unique way to hold and release energy. Knowing their basics makes comparisons clearer.
How Agm Batteries Work
AGM stands for Absorbent Glass Mat. It uses a fiberglass mat to hold acid. This mat keeps acid from spilling inside the battery. When the battery charges, chemical reactions create electricity. The process stores energy in lead plates. When in use, the battery releases this energy as power. AGM batteries are sealed and maintenance-free.
How Lithium Batteries Work
Lithium batteries use lithium ions to store energy. These ions move between two electrodes during charging and discharging. The battery has a liquid or gel electrolyte to help ions move. The electrodes are made from different materials to hold lithium. This movement of ions creates electric current. Lithium batteries are lighter and hold more energy.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Power Capacity
Power capacity defines how much energy a battery can store and deliver. It affects how long your device or vehicle runs before needing a recharge. Understanding power capacity helps choose the right battery for specific needs. AGM and lithium batteries differ significantly in this area.
Energy Density Comparison
Energy density measures how much energy fits in a battery’s size or weight. Lithium batteries have higher energy density than AGM batteries. They store more energy in a smaller, lighter package. This makes lithium batteries better for compact or portable devices. AGM batteries are heavier and bulkier for the same energy amount. They suit applications where weight is less important.
Discharge Rates
Discharge rate shows how fast a battery can release energy. Lithium batteries handle higher discharge rates without damage. They provide steady power even under heavy load. AGM batteries have lower discharge rates and can overheat if pushed too hard. This limits their use in high-power situations. Choosing the right discharge rate ensures reliable battery performance.
Performance Factors
Performance factors play a key role in choosing between AGM and lithium batteries. These factors affect how well the battery works in different conditions. Understanding them helps pick the right battery for specific needs.
Charge Time Differences
AGM batteries take longer to charge compared to lithium batteries. Charging an AGM battery fully can take several hours. Lithium batteries charge much faster, often in less than half the time. This speed makes lithium batteries better for quick turnarounds. Faster charging saves time and keeps devices running longer.
Temperature Tolerance
AGM batteries handle cold temperatures better than lithium batteries. They perform well in chilly weather without much loss in capacity. Lithium batteries work best in moderate temperatures and may lose power in extreme cold. Both types can get damaged if exposed to very high heat. Choosing a battery with the right temperature tolerance is vital for reliable performance.
Lifespan And Durability
Lifespan and durability are key factors in choosing between AGM and lithium batteries. These qualities determine how long a battery lasts and how well it handles use. Understanding these aspects helps pick the best battery for your needs.
Cycle Life Comparison
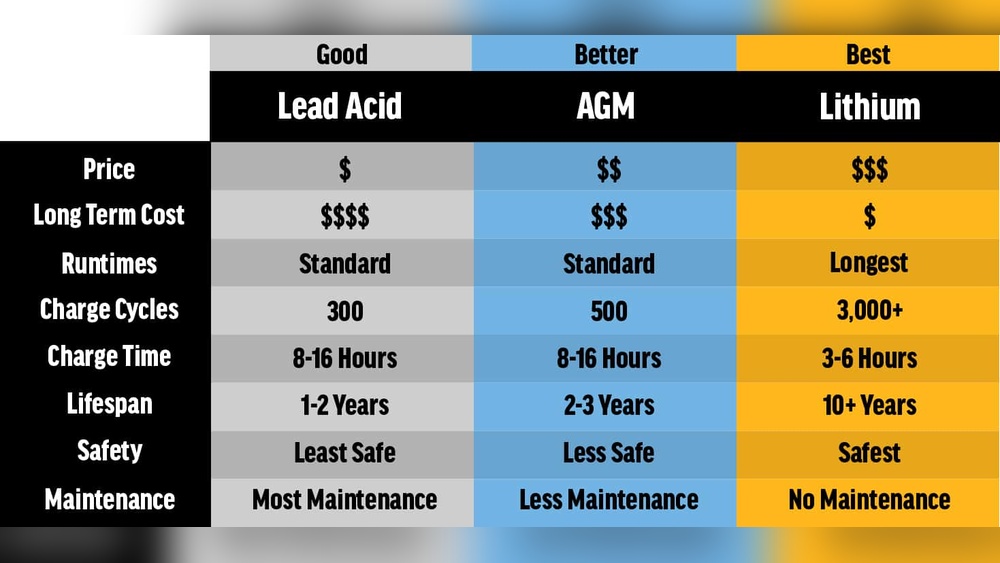
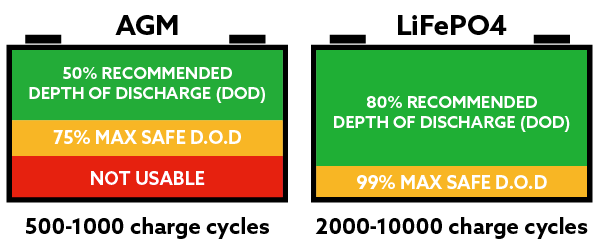
AGM batteries typically last for about 300 to 500 cycles. Each cycle means one full charge and discharge. Lithium batteries offer a higher cycle count, often between 2,000 and 5,000 cycles. This means lithium batteries last much longer under regular use. They maintain capacity better over time, giving more reliable power. AGM batteries lose capacity faster after many cycles.
Maintenance Needs
AGM batteries require some care to keep working well. They should not stay fully discharged for long. Checking water levels is not needed, unlike flooded batteries, but charging must be managed carefully. Lithium batteries need less maintenance. They do not suffer from sulfation, a common AGM problem. Lithium batteries can be stored longer without damage. This makes them easier to use in many settings.
Safety Considerations
Safety is a key factor when choosing between AGM and lithium batteries. Both types store power but differ in risks and protections. Understanding these safety aspects helps you make a wise decision.
Risk Of Leakage Or Explosion
AGM batteries use a sealed design to reduce acid leaks. They hold sulfuric acid in glass mats, making spills rare. Yet, extreme heat or damage can cause leaks or pressure build-up. This might lead to explosion or acid burns.
Lithium batteries have a higher energy density. This means more power in a smaller space. But, they can overheat and catch fire if damaged or poorly charged. A thermal runaway event can cause explosions or toxic gas release.
Built-in Safety Features
AGM batteries have valves to release pressure safely. Their design limits acid exposure and prevents spills. They need no extra maintenance to stay safe.
Lithium batteries include electronic safety circuits. These protect against overcharging, overheating, and short circuits. Many use strong casing to avoid physical damage. These features help reduce fire and explosion risks.
Cost And Value
Cost and value are key factors when choosing between AGM and lithium batteries. Both types serve different needs and budgets. Understanding their costs helps make a smart choice.
Initial Investment
AGM batteries have a lower upfront price. They are cheaper to buy and easy to find. Lithium batteries cost more at the start. Their price is higher due to advanced technology. This can be a barrier for some buyers.
Long-term Savings
Lithium batteries last much longer than AGM. They need fewer replacements over time. This saves money in the long run. Lithium also charges faster and holds power better. AGM batteries wear out quicker and need more care. This can increase maintenance costs over time.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of batteries is a crucial factor for many users. Choosing between AGM and lithium batteries involves understanding their effects on nature. Batteries can affect the environment during production, use, and disposal. This section explains the key environmental aspects of both types.
Recyclability
AGM batteries are lead-acid batteries. Lead is a heavy metal that can harm the environment if not handled properly. Recycling AGM batteries is common and well-established. Most of the lead and plastic parts can be reused. This reduces waste and pollution. Recycling rates for AGM batteries are high compared to many other types.
Lithium batteries contain valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Recycling lithium batteries is more complex. The process requires advanced technology and is less common. Many lithium batteries end up in landfills, causing environmental risks. Efforts to improve lithium battery recycling are growing fast.
Eco-friendly Factors
AGM batteries use lead and acid, which can be toxic. If broken, they can leak harmful chemicals into the soil and water. They also have a shorter lifespan, needing more replacements. This increases the total environmental footprint over time.
Lithium batteries are lighter and hold more energy. They usually last longer than AGM batteries. Longer life means fewer replacements and less waste. Lithium batteries do not contain lead or acid, reducing some pollution risks. Still, mining for lithium and other metals affects ecosystems and water supplies.
Credit: www.keefmarine.co.uk
Best Use Cases
Choosing between AGM and lithium batteries depends on the task at hand. Each type shines in different situations. Understanding their best use cases helps you pick the right one.
Applications Suited For Agm
AGM batteries work well in vehicles like cars and motorcycles. They handle cold weather and vibrations better. They require less maintenance and are spill-proof. Ideal for backup power in homes and offices. They perform reliably in solar energy storage systems. Also good for wheelchairs and small boats.
Applications Suited For Lithium
Lithium batteries are perfect for electric cars and drones. They offer longer life and lighter weight. Great for portable electronics and power tools. They charge faster and provide more power. Used in large solar setups and off-grid homes. Also popular in marine and RV applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Differences Between Agm And Lithium Batteries?
AGM batteries use lead-acid technology, while lithium batteries use lithium-ion cells. Lithium batteries are lighter, last longer, and charge faster. AGM batteries are heavier, cheaper, and more resistant to cold temperatures. Both have specific uses depending on power needs and budget.
Which Battery Type Is Better For Deep Cycle Use?
Lithium batteries are better for deep cycle use due to their higher cycle life and efficiency. AGM batteries have fewer cycles and can degrade faster under deep discharge. Lithium also maintains voltage better during discharge, offering consistent power for longer periods.
Are Agm Batteries Safer Than Lithium Batteries?
AGM batteries are generally safer because they are sealed and less prone to overheating. Lithium batteries require built-in protection circuits to prevent overcharging and overheating. Proper handling and quality manufacturing improve safety for both types.
How Does Cost Compare Between Agm And Lithium Batteries?
AGM batteries are usually cheaper upfront but have a shorter lifespan. Lithium batteries have a higher initial cost but save money long-term due to durability and efficiency. Consider total cost of ownership when choosing between them.
Conclusion
Both AGM and lithium batteries have clear strengths and weaknesses. AGM batteries cost less and work well in cold weather. Lithium batteries last longer and weigh much less. Choosing depends on your needs, budget, and how you use the battery.
Think about what matters most: price, weight, or lifespan. Each type fits different uses. Knowing these basics helps you pick the right battery with confidence. Simple and smart decisions lead to better results.