Electric Vs Gas Generator: Which is the Best for You?
When it comes to generators, two popular choices stand out: electric and gas. Both have their unique advantages and drawbacks.
Generators are essential tools for backup power. Whether for home use or outdoor activities, choosing the right type can be challenging. Electric generators are known for their quiet operation and low maintenance. In contrast, gas generators are praised for their power and reliability.
Understanding the key differences can help you make an informed decision. This comparison will highlight the main features, benefits, and limitations of each type. So, if you’re unsure which generator suits your needs best, read on to discover the pros and cons of electric and gas generators.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Electric Generators
Electric generators are a popular choice for providing backup power in homes and businesses. They convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, ensuring your essential appliances keep running during a power outage. Understanding how these generators work and their pros and cons can help you decide if they are the right fit for you.
How Electric Generators Work
An electric generator operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Inside the generator, a rotor spins within a magnetic field. This motion creates a flow of electric current in the coil of wire. The current is then directed to your electrical system, providing power to your appliances.
The generator’s engine, which runs on fuel such as diesel or natural gas, drives the rotor. The engine’s motion is what creates the mechanical energy needed for the electric current. This process is efficient and can provide a steady supply of electricity.
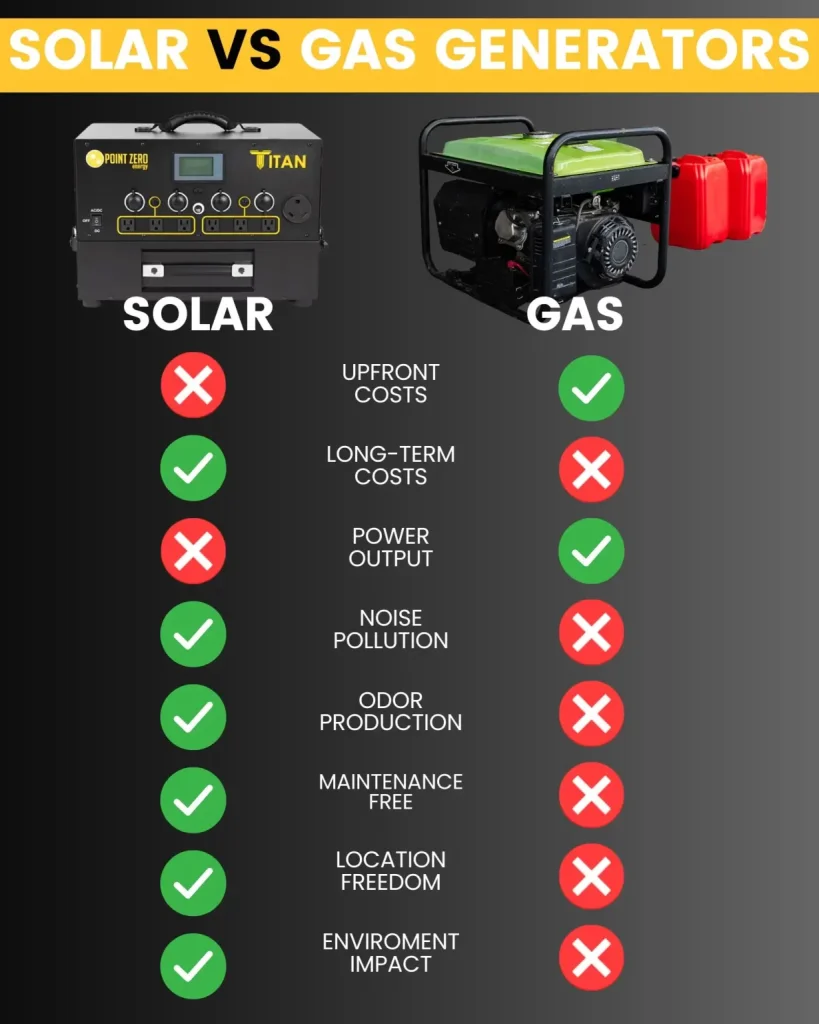
Pros Of Electric Generators
- Quiet Operation: Electric generators produce less noise compared to gas generators.
- Environmentally Friendly: They produce fewer emissions, making them a greener option.
- Low Maintenance: Electric generators require less upkeep and fewer repairs.
- Easy to Use: Simple controls make them user-friendly for all.
Cons Of Electric Generators
- Higher Initial Cost: Electric generators tend to be more expensive upfront.
- Limited Fuel Options: They may be restricted to certain types of fuel.
- Power Output: They often provide less power than gas generators.

Credit: www.earthtechproducts.com
Gas Generators
Gas generators are reliable power sources for various situations. Many households and businesses prefer them for their efficiency and power output. They use gasoline or natural gas to generate electricity. This type of generator is especially useful in areas with frequent power outages.
How Gas Generators Work
Gas generators convert fuel into electrical power. They have an engine that burns fuel to create mechanical energy. This energy then spins an alternator to produce electricity. The generator’s engine needs regular maintenance to run smoothly. Fuel is stored in a tank and delivered to the engine as needed.
Pros Of Gas Generators
Gas generators are highly efficient. They produce a lot of power for their size. This makes them ideal for larger homes and businesses. They are also portable. You can easily move them to different locations. Gas generators are readily available. You can find them in most hardware stores.
Cons Of Gas Generators
Gas generators can be noisy. This can be a problem in residential areas. They also require regular maintenance. This includes changing the oil and checking the spark plugs. Gas generators emit fumes. These fumes can be harmful if not properly ventilated. Fuel storage can be another issue. Gasoline can be dangerous to store in large quantities.
Cost Comparison
Choosing between an electric and gas generator involves many factors. One important aspect is the cost. Understanding the cost differences can help you make an informed decision. Let’s explore the costs associated with each type.
Initial Costs
Electric generators often have higher initial costs. They use advanced technology and require more components. These generators are usually quieter and cleaner. Gas generators tend to be cheaper upfront. They are simpler in design and use widely available parts.
Operational Costs
Operational costs differ significantly. Electric generators usually cost less to run. They use electricity, which is often cheaper than fuel. Gas generators need regular fuel purchases. Fuel prices can fluctuate, making costs unpredictable. Electric generators are more consistent in this regard.
Maintenance Costs
Maintenance is another crucial factor. Electric generators require less maintenance. They have fewer moving parts and do not need oil changes. Gas generators need more frequent upkeep. Oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug checks are common. This increases the overall maintenance cost.
Environmental Impact
Both electric and gas generators have distinct effects on the environment. Understanding these impacts helps you make informed decisions. This section covers the emissions and pollution, and the energy efficiency of each generator type.
Emissions And Pollution
Gas generators emit harmful gases. They release carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These pollutants contribute to air pollution and climate change. Gas generators also produce particulate matter, which harms human health.
Electric generators are cleaner. They do not produce emissions during operation. However, their environmental impact depends on how the electricity is generated. Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are the cleanest. Coal or natural gas power plants still produce emissions.
Energy Efficiency
Electric generators convert energy efficiently. They have fewer moving parts. This reduces energy loss and increases efficiency. When powered by renewable sources, they have an even lower environmental impact.
Gas generators are less efficient. They lose energy through heat and friction. Fuel combustion in gas generators is not 100% efficient. This results in higher fuel consumption and more emissions.
The table below compares the energy efficiency of electric and gas generators:
| Generator Type | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Electric | High (especially with renewables) |
| Gas | Lower due to combustion losses |
Performance And Reliability
Electric generators offer quiet operation and low maintenance, ensuring reliable performance. Gas generators provide more power for longer durations, suitable for heavy-duty tasks.
Generators play a vital role in providing power during outages. Choosing between an electric and gas generator depends on their performance and reliability. Both types have their strengths and weaknesses. This section explores the differences in power output and durability.Power Output
Electric generators provide consistent power. They are ideal for smaller appliances and electronics. They have a limited power output, making them less suitable for heavy-duty tasks. Gas generators, on the other hand, offer higher power output. They can handle larger appliances and tools. This makes them a better choice for power-intensive tasks.Durability And Lifespan
Electric generators usually require less maintenance. They have fewer moving parts, reducing the chance of mechanical failure. This often results in a longer lifespan. Gas generators require regular maintenance. They have engines that need oil changes and other upkeep. This can affect their durability over time. Despite this, gas generators are built tough. They can withstand rough conditions and heavy use. This makes them reliable for long-term use. “`Ease Of Use
Choosing between an electric and a gas generator often depends on ease of use. Factors like installation, setup, and user-friendly features play significant roles. Both types offer unique advantages. Understanding these can help you decide which suits your needs better.
Installation And Setup
Electric generators are usually easier to install. They often require minimal setup. Plug them into an outlet, and they are ready. Gas generators, on the other hand, might need more work. Connecting to a fuel source and proper ventilation is crucial. This makes the setup process more complex.
User-friendly Features
Electric generators tend to have more user-friendly features. They often come with remote control options. This allows easy operation from a distance. Gas generators might have more manual controls. You may need to start them with a pull cord. This can be more challenging for some users.
Electric models often include quieter operation. This can be a big plus in residential areas. Gas generators can be noisier. They may not be suitable for all environments. Additionally, electric generators usually require less maintenance. Gas generators need regular fuel checks and oil changes.
Suitability For Different Needs
Choosing between an electric and gas generator depends on your specific needs. Each type has its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these differences helps you make the right choice. Let’s explore their suitability for different situations.
Home Use
Electric generators are quiet and clean. They are ideal for home use. They produce no fumes, making them safe for indoor use. Electric generators are easier to maintain. They also require less maintenance compared to gas generators.
Gas generators are powerful and reliable. They can handle larger loads. They are suitable for homes with high power needs. But, they produce noise and fumes. It is best to use them outdoors or in well-ventilated areas.
Commercial Use
For commercial use, gas generators are often preferred. They deliver higher power output. This makes them suitable for businesses. They can handle heavy machinery and multiple devices. Gas generators are durable and robust. They can run for long periods without issues.
Electric generators can also be used commercially. They are best for small businesses. Businesses that need quiet, clean energy can benefit from them. They are easy to install and maintain. But, they may not meet the power needs of larger operations.
Emergency Backup
In emergencies, reliability is key. Gas generators provide consistent power. They are reliable during power outages. They can run for long durations. Gas generators are great for long-term backup power.
Electric generators are also useful in emergencies. They are great for short-term use. They start quickly and provide instant power. They are ideal for quick, temporary power needs. But, they may not last as long as gas generators during extended outages.
Credit: www.pointzeroenergy.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Is Better, Electric Or Gas Generator?
Electric generators are quieter, cleaner, and require less maintenance. Gas generators are more powerful and suitable for heavy-duty tasks. Choose based on your needs.
Are Electric Generators Safer Than Gas Generators?
Yes, electric generators are generally safer. They don’t produce harmful emissions or require flammable fuel, reducing the risk of accidents.
Do Gas Generators Last Longer Than Electric Generators?
Gas generators typically have a longer lifespan when used and maintained properly. However, electric generators have fewer moving parts and can be more reliable.
Which Generator Is More Cost-effective?
Gas generators usually have a lower initial cost but higher operational costs. Electric generators are more expensive upfront but cheaper to run.
Conclusion
Choosing between an electric and gas generator depends on your needs. Electric generators are quieter and eco-friendly. Gas generators are more powerful and reliable during long outages. Consider your power needs, budget, and environmental concerns. Both options have their pros and cons.
Analyze what suits your situation best. Prioritize safety and efficiency. With the right generator, you can ensure a continuous power supply. Make an informed decision for peace of mind.







